Sachin Sulkunte

University of Maryland at College Park
- B.S. Computer Engineering 2024
- Minor in Robotics and Autonomous
Systems
- Cybersecurity Honors Program
View My LinkedIn Profile
View My Github Profile
Contact Me:
E: sulkunte@gmail.com
C: (301) 605-0719
Universal-Robots UR3 Robotic Arm
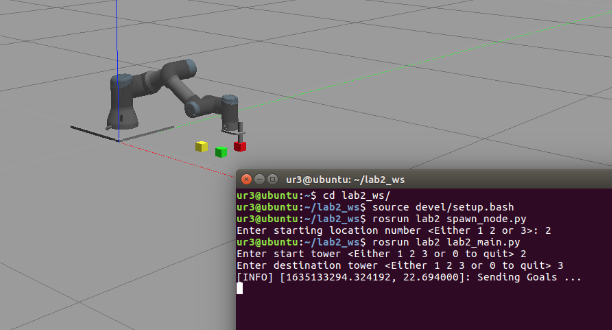
Project description: I completed this project as part of my coursework in the Robotics and Autonomous Systems Minor program. The project involved solving the inverse kinematic and forward kinematic equations for the UR3, a 6-DOF robotic arm.
1. Solving the transformation matrices for forward kinematics
The transformation matrices were solved by calculating the screw axis matrices for each joint of the arm. These matrices were multiplied together with the angle (theta) value in order to get the final transformation matrix.
def lab_fk(theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, theta5, theta6):
# =========== Implement joint angle to encoder expressions here ===========
print("Foward kinematics calculated:\n")
theta = np.array([theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4,theta5,theta6])
T = np.eye(4)
M, S = Get_MS()
S_mat1 = np.array([[0, -S[0][2], S[0][1], S[0][3]], [S[0][2],0,-S[0][0], S[0][4]], [-S[0][1], S[0][0], 0, S[0][5]], [0,0,0,0]])
exp1 = expm(S_mat1*theta1)
2. Implementing a gripper in ROS and Simulating in Gazebo
The program utilizes ROS to create nodes for publishers and subscribers to enable communication. Gazebo is used for simulation purposes. A URDF file defines the UR3 robot structure and ROS is used to control the robot’s movements.
def main():
global home
# Initialize ROS node
rospy.init_node('lab3node')
# Initialize publisher for ur3/command with buffer size of 10
pub_command = rospy.Publisher('ur3/command', command, queue_size=10)
# Initialize subscriber to ur3/position & ur3/gripper_input and callback fuction
# each time data is published
sub_position = rospy.Subscriber('ur3/position', position, position_callback)
sub_input = rospy.Subscriber('ur3/gripper_input', gripper_input, input_callback)
3. Running program on live robot
The next stage of the class involves implementing my code on a physical UR3 robot in a lab environment. This page will be updated at that point.
move_arm(pub_cmd, loop_rate, Q[start_loc][start_height][1], robot_states, params)
move_arm(pub_cmd, loop_rate, Q[start_loc][start_height][0], robot_states, params)
gripper(pub_cmd, loop_rate, True, robot_states, params)
time.sleep(0.5)
if robot_states.digital_in_0 == 0:
print("No block detected. Exiting program.")
sys.exit()
move_arm(pub_cmd, loop_rate, Q[start_loc][start_height][1], robot_states, params)
move_arm(pub_cmd, loop_rate, Q[end_loc][end_height][1], robot_states, params)
move_arm(pub_cmd, loop_rate, Q[end_loc][end_height][0], robot_states, params)
gripper(pub_cmd, loop_rate, False, robot_states, params)
time.sleep(0.5)