Sachin Sulkunte

University of Maryland at College Park
- B.S. Computer Engineering 2024
- Minor in Robotics and Autonomous
Systems
- Cybersecurity Honors Program
View My LinkedIn Profile
View My Github Profile
Contact Me:
E: sulkunte@gmail.com
C: (301) 605-0719
Autonomous Vehicle Project
Video:
Project description:
I completed this project in order to apply a variety of skills towards the development of a complex electromechanical system with autonomous capabilities. This “self-driving car” was built as a 4-motor differential drive robot for mechanical simplicity. A Jetson Nano is used for high-level decision making based on input from a RGBD-camera (Kinect Sensor). An Arduino is used for low-level motor control - receiving instructions via serial connection from the Nano. The system uses ROS for efficient feature implementation, with individual nodes representing features such as object detection and lane detection. RViz is used for 3D visualization. The controller subscribes to these nodes and makes steering and throttle decisions based upon a rule-based motion planning scheme. The RRT path planning algorithm is used for navigation to desired waypoints.
High-Level Project Presentation
MotionPlanningForAutonomousMobileRobots.pdf
Overall Design Process:
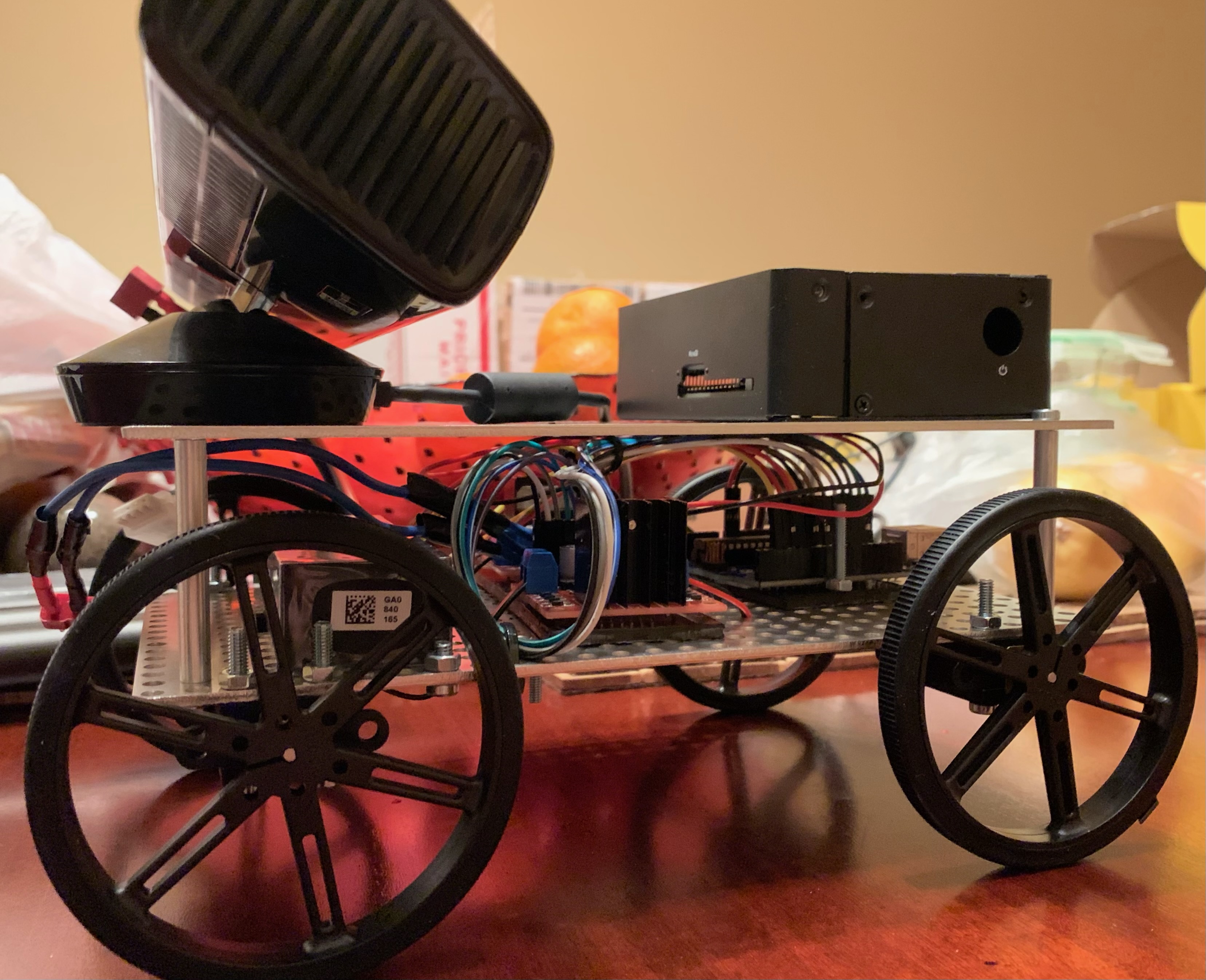
1. Physical Assembly of Robot
- Soldered connections between H-bridges and motors
- Connected to Arduino and Jetson Nano
- Assembled onto two-tiered frame
2. Initial Work with Camera
- Communication between Kinect camera and Jetson Nano using OpenKinect’s libfreenect library to get RGB and Depth data
- Created ROS node that publishes to ROS topic
- Visualized raw point cloud data in RViz by reading from ROS topic
3. SLAM Implementation
- Utilized ORB-SLAM2 algorithm due to real-time capabilities and strong performance in variety of environments
- ROS node running ORB-SLAM2 is subscribed to camera topic to get RGB-D data
4. Low-Level Controller (Arduino)
- Utilized rosserial module for serial communication to Arduino
- Created subscriber node to /cmd_vel that reads in move commands to Arduino
- Developed PID controller for motors
5. High-Level Controller (Jetson Nano)
- Implemented finite state machine using SMACH package in ROS
- Uses object recognition results and ultrasonic sensor data to inform next state
6. Path Planning
- Used RRT algorithm to solve for possible path through complete map given start and end points
- Robot follows path (non-optimal) around objects
Implemented Features:
- Rule-Based Motion Planning with Object Recognition and Detection
- SLAM
- PID Controller
- Path Planning using RRT Algorithm
Future Features
- GUI for Simple Mapping and Setting Waypoints
- PID Control Alternatives - Predictive Functional Control
- Automated Parking
- Ackermann Steering System
- End-to-End Lane Detection
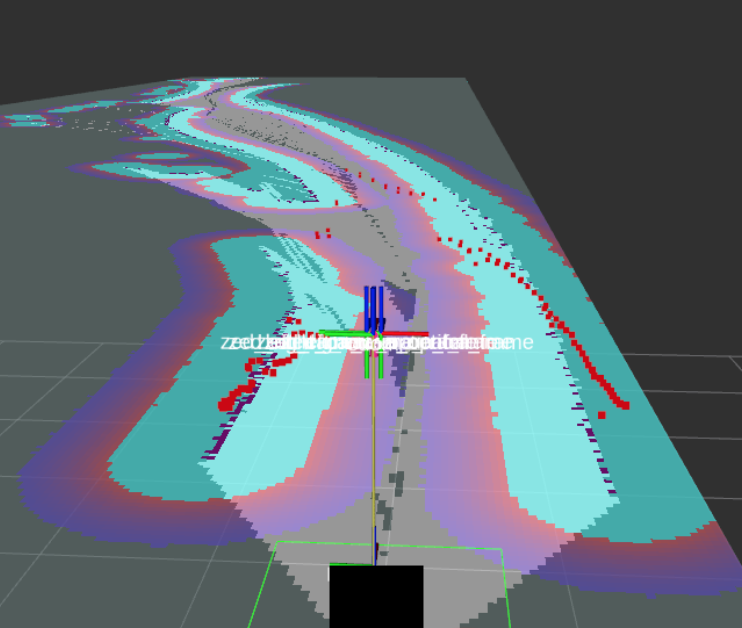
RViz Visualization:
Robot Platform with Kinect Sensor, Jetson Nano, and Arduino Uno:

Sample Map
